anatomy
How does the back work?
The human spine (also known as the spine) consists of 33 or 34 vertebrae, with an intervertebral disc between each two vertebrae. From top to bottom, the vertebral column consists of: • 7 cervical vertebrae (cervical vertebral column) • 12 thoracic vertebrae (thoracic vertebral column) • 5 lumbar vertebrae (lumbar vertebral column) • the sacrum, a fusion of 5 vertebrae (sacrum) • the tailbone or tailbone, a tailbone Greening of 4 or 5 vertebrae (coccygeus)
Vertebrae
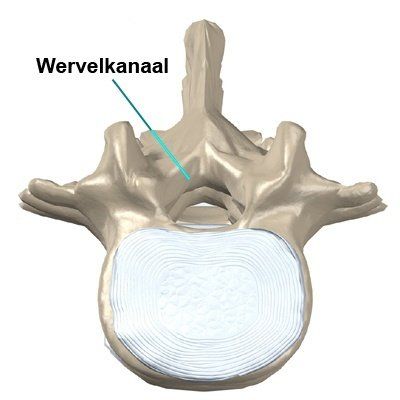
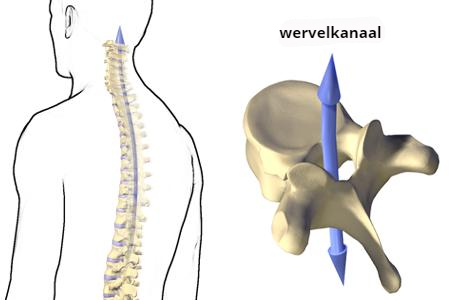
Because of the shape of the vertebrae and because they are positioned above each other, a hollow channel is created that runs through the vertebral column.
Vertebral canal
This channel is called the spinal canal, within which the spinal cord is located. The vertebrae protect the spinal cord and carry the weight. The human spine has an S-shape. This form isolates shocks that occur during walking or running from the sensitive brain. The curvatures in this s-form are indicated by the terms lordosis and kyphosis. A lordosis is hollow, such as in the neck and lower back, and a kyphosis is convex, as in the chest (thorax) and the sacrum (sacrum).
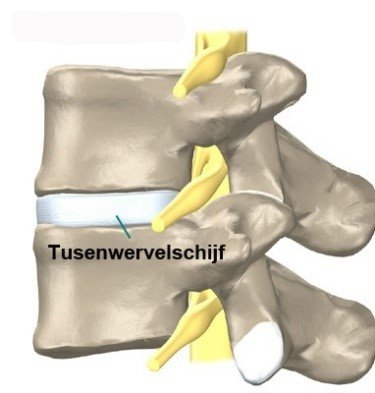
Intervertebral discs
The spine consists of 24 vertebrae. There is an intervertebral vertebra between every two vertebrae. The intervertebral vertebra is also called a discus. This disc can be compared to a kind of air cushion. This air cushion, or intervertebral disc, absorbs the shocks of the entire spinal column and makes it possible to move in the spinal column. So the intervertebral disc provides shock absorption and has a hinge function.
The intervertebral discs are the most vulnerable part of the spinal column and are the first to break!
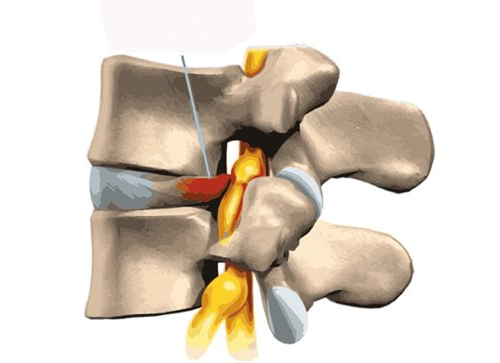

How does weight collection work?
The pressure on the intervertebral disc (for example when sitting, lifting, carrying) is converted into a tensile stress on the outer slats of the disc (annulus fibrosus).
Compare it to sitting on a ball, the compressive stress of the weight is converted into a tensile stress on the plastic of the ball. If the person is overweight, the ball will tear open.


'Flat-tire syndrome'
A 'torn' (= hernia) ball is similar to a flat tire. This is called the 'Flat-tire' syndrome. This 'flat tire' ensures a reduced stability of the spine. "Try to go around the corner with a flat tire by bike."







